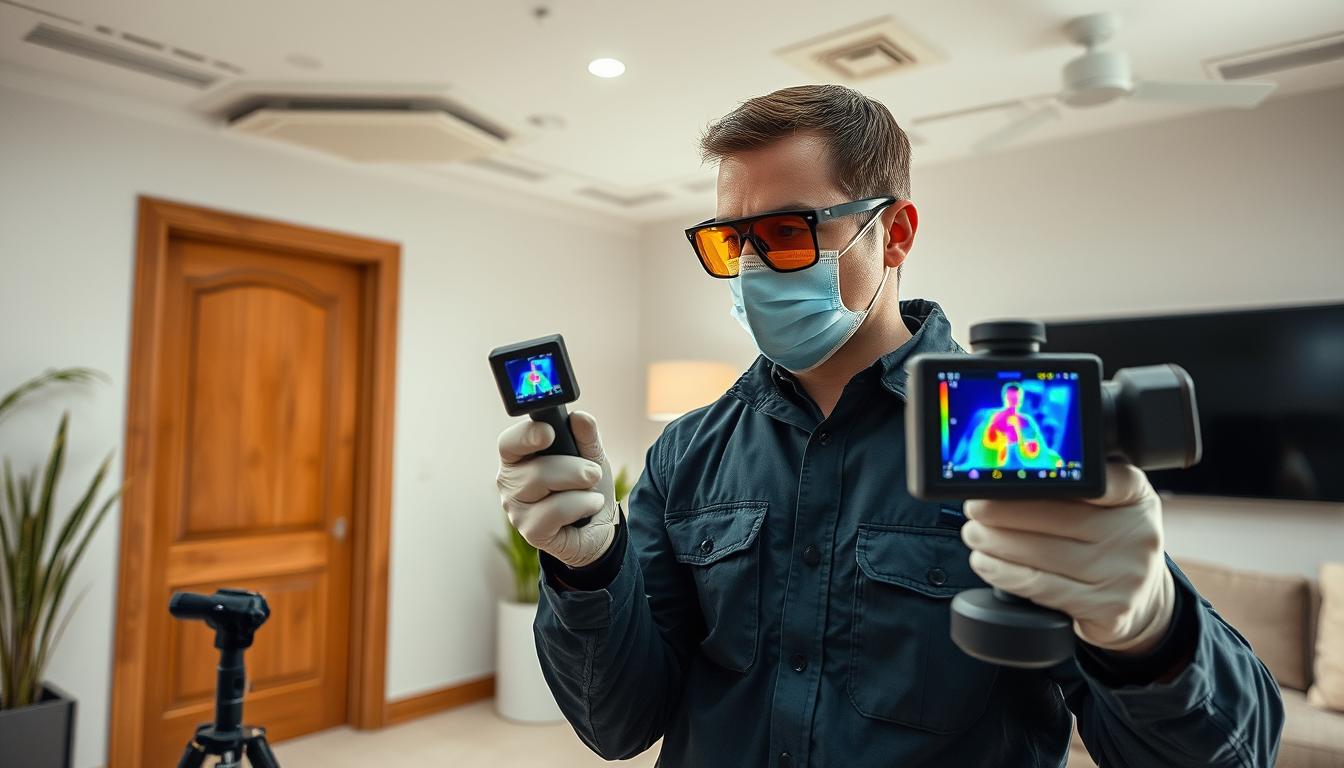
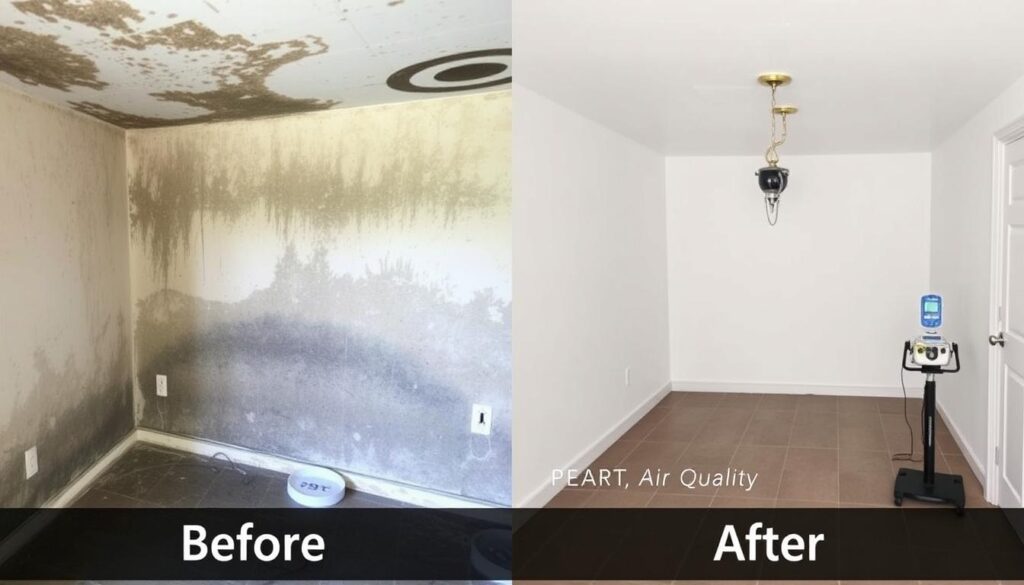
The landscape of mold remediation has evolved dramatically in recent years, with advanced technologies and indoor air quality considerations taking center stage. As we become more aware of how mold affects our health and well-being, the approach to remediation has shifted from simply removing visible mold to implementing comprehensive solutions that address the root causes while ensuring the air we breathe remains clean and safe. This integration of cutting-edge technology with indoor air quality priorities represents the future of effective, sustainable mold remediation.
Understanding Modern Mold Remediation: A Technological Revolution
Traditional mold remediation often focused solely on removing visible mold growth, sometimes missing hidden problems and failing to address underlying causes. Modern approaches have revolutionized this field by incorporating advanced detection methods, precise removal techniques, and comprehensive air quality management. This technological evolution has transformed remediation from a reactive cleanup process into a proactive, health-focused service.
The Evolution of Mold Detection Technology
Today’s mold remediation professionals utilize sophisticated tools that go far beyond visual inspection. Thermal imaging cameras can detect temperature variations that indicate moisture—the primary catalyst for mold growth—behind walls and under floors. Moisture meters provide precise readings of humidity levels in building materials, while advanced air sampling devices collect and analyze airborne mold spores that would otherwise remain invisible.
These technologies allow remediation specialists to identify the full extent of mold problems before remediation begins, ensuring that no affected areas are overlooked. By mapping moisture patterns and identifying hidden mold colonies, technicians can develop comprehensive remediation plans that address both visible and concealed issues.
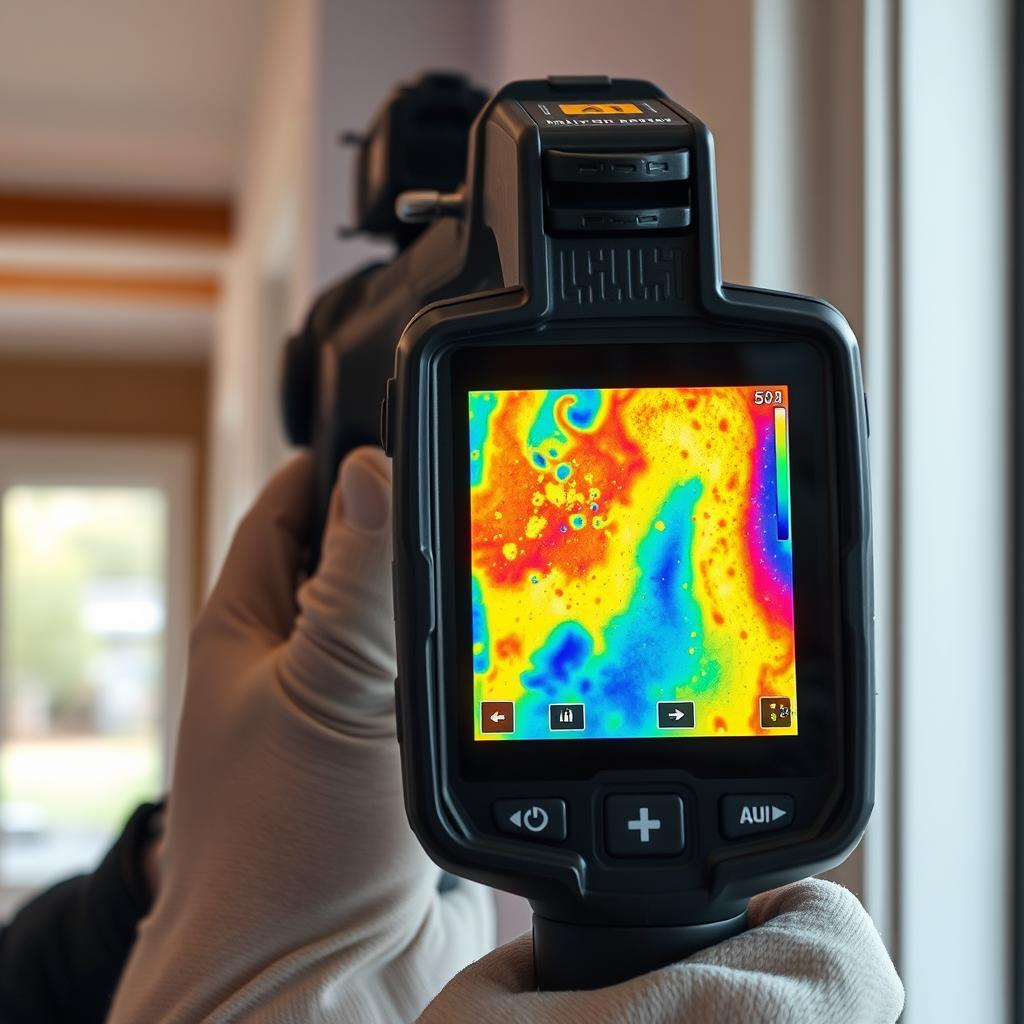

AI-Driven Assessment and Remediation Planning
Artificial intelligence has entered the mold remediation field, offering unprecedented precision in assessment and planning. AI algorithms can analyze environmental data, moisture readings, and air quality measurements to predict mold growth patterns and identify risk factors that might be missed by human inspection alone. These systems can also develop optimized remediation protocols based on the specific mold species present, building materials affected, and environmental conditions.
The integration of advanced technologies in mold remediation doesn’t just improve efficiency—it fundamentally enhances our ability to create healthier indoor environments by addressing problems at their source.
Prioritizing Indoor Air Quality in the Remediation Process
Modern mold remediation places indoor air quality at the forefront of the process, recognizing that airborne mold spores and remediation byproducts can significantly impact occupant health. This shift in focus has led to the development of containment and filtration systems specifically designed to protect and improve air quality during and after remediation.
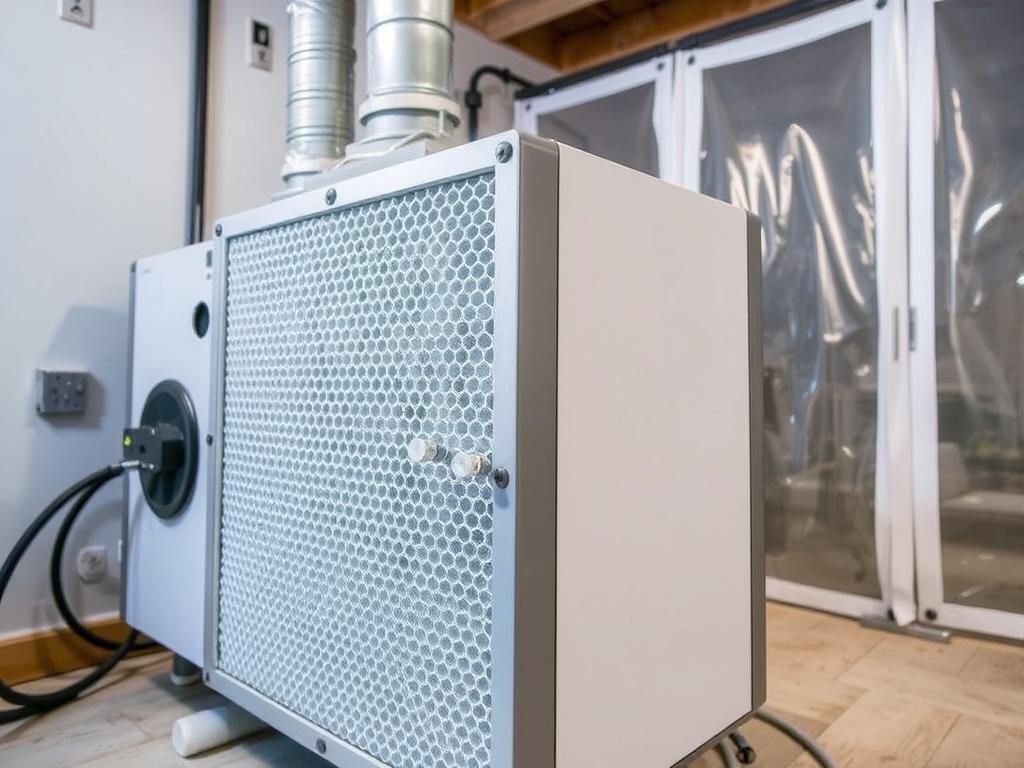

Advanced Containment and Negative Air Pressure
To prevent cross-contamination during remediation, technicians implement sophisticated containment systems that isolate affected areas. These systems use specialized barriers and negative air pressure machines to ensure that mold spores and dust don’t spread to clean areas of the building. The negative pressure environment created by these systems forces air to flow into the containment area rather than out of it, effectively trapping contaminants.
Modern containment systems are often equipped with pressure monitoring devices that alert technicians to any breaches in the containment barrier, allowing for immediate correction and maintaining air quality protection throughout the remediation process.
HEPA Filtration and Air Scrubbing Technology
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filtration represents one of the most significant technological advances in protecting indoor air quality during mold remediation. HEPA air scrubbers can capture particles as small as 0.3 microns—including mold spores, dust, and allergens—with 99.97% efficiency. These systems continuously filter the air within containment areas, progressively reducing airborne contaminants throughout the remediation process.
Advanced air scrubbers now incorporate multiple filtration stages, including activated carbon filters that capture volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the remediation process. This multi-stage approach ensures comprehensive air purification that addresses particulates, microbial contaminants, and chemical odors.
Eco-Friendly Antimicrobial Treatments and Sustainable Practices
The integration of advanced technologies in mold remediation extends to the development and application of eco-friendly treatments that effectively eliminate mold while minimizing environmental impact and protecting indoor air quality. These innovative approaches represent a significant departure from traditional chemical-heavy methods.
Botanical and Enzymatic Remediation Agents
Modern remediation increasingly utilizes plant-based and enzymatic antimicrobial treatments that break down mold at the cellular level without introducing harmful chemicals into the indoor environment. These solutions are derived from natural compounds like thyme oil, citrus extract, and specialized enzymes that target mold cells while remaining safe for humans and pets.
Unlike harsh chemical alternatives, these botanical solutions don’t release VOCs or leave toxic residues that can compromise indoor air quality. They’re particularly valuable in sensitive environments like schools, healthcare facilities, and homes with vulnerable occupants.

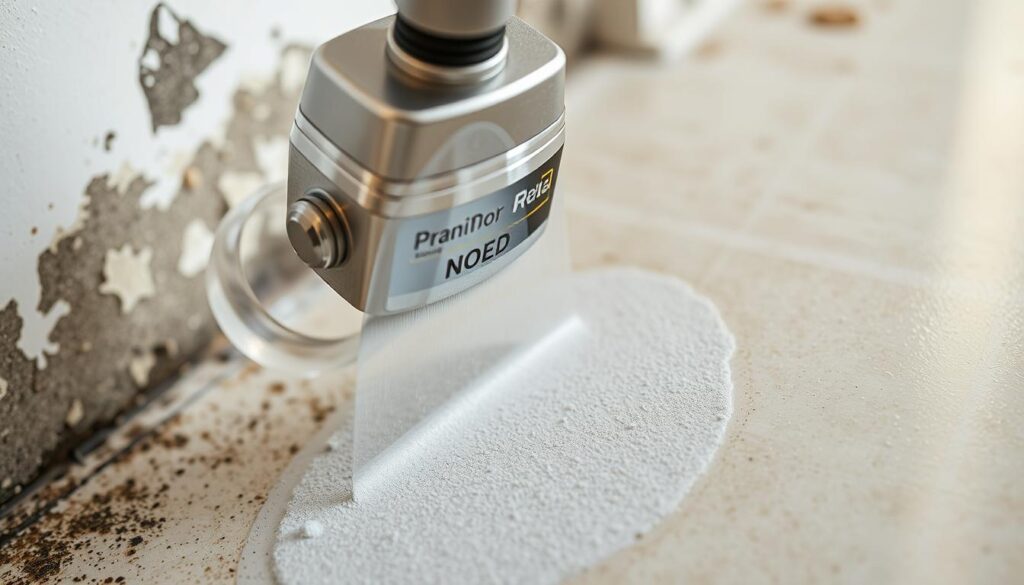
Dry Ice and Steam Remediation Technologies
Advanced physical remediation methods like dry ice blasting and precision steam cleaning represent cutting-edge approaches that minimize chemical use while effectively removing mold. Dry ice blasting uses compressed air to propel solid carbon dioxide particles at high speeds, removing mold without damaging underlying surfaces. The carbon dioxide sublimates (changes directly from solid to gas), leaving no secondary waste and eliminating the need for chemical cleaners.
Similarly, high-temperature steam systems can reach temperatures that instantly kill mold spores without requiring additional antimicrobial treatments. These methods significantly reduce the introduction of chemicals into the indoor environment, supporting better air quality during and after remediation.
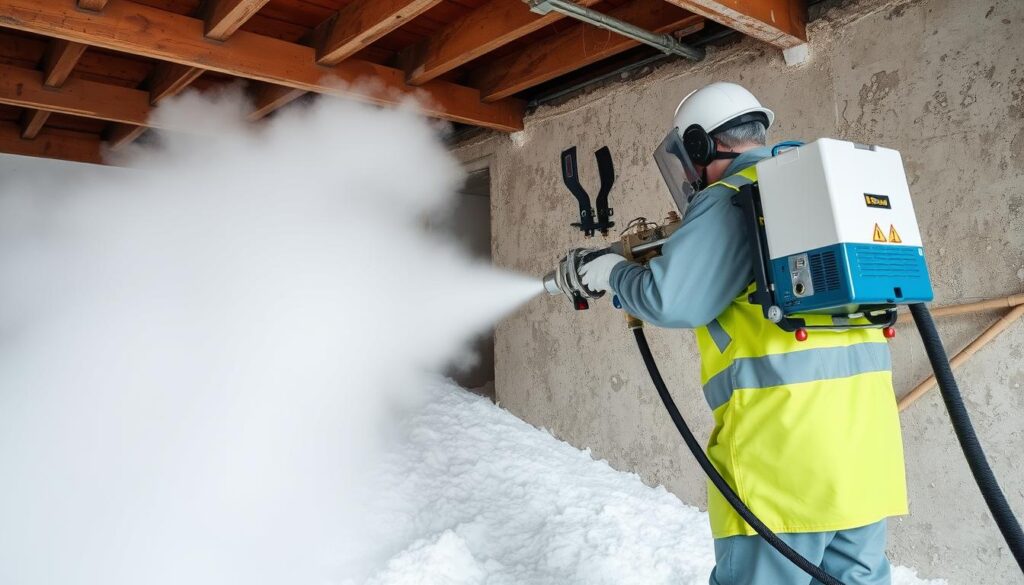

Real-Time Air Quality Monitoring During Remediation
One of the most significant technological advances in modern mold remediation is the implementation of continuous, real-time air quality monitoring throughout the remediation process. This approach ensures that indoor air quality is maintained at optimal levels and allows for immediate adjustments if contaminant levels rise.
Particulate and VOC Monitoring Systems
Advanced monitoring systems track multiple air quality parameters simultaneously, including particulate matter concentrations, volatile organic compound levels, relative humidity, and temperature. These systems provide continuous data streams that allow remediation professionals to verify the effectiveness of their containment and filtration systems in real-time.
When integrated with cloud-based platforms, these monitoring systems can send alerts if air quality parameters exceed predetermined thresholds, enabling immediate corrective action. This technology ensures that remediation activities don’t inadvertently compromise indoor air quality.
Data-Driven Verification of Remediation Success
Beyond monitoring during active remediation, advanced air quality testing provides objective verification that remediation efforts have successfully resolved mold issues. Post-remediation verification using laboratory analysis of air samples confirms that mold spore concentrations have returned to normal levels and that no new contaminants have been introduced during the remediation process.
This data-driven approach provides property owners with documented evidence of successful remediation and creates a baseline for future air quality monitoring. Many remediation companies now offer ongoing monitoring services that can detect changes in air quality that might indicate returning moisture or mold problems.
Integrating Advanced Ventilation Systems in Remediation Planning
Modern mold remediation extends beyond addressing existing mold to implementing preventive measures that maintain healthy indoor air quality long-term. Advanced ventilation systems play a crucial role in this approach, helping to control moisture levels and ensure proper air exchange.
Whole-House Ventilation Solutions
Comprehensive remediation plans often include the installation or upgrading of whole-house ventilation systems that provide continuous air exchange. These systems introduce fresh outdoor air while exhausting stale indoor air, helping to maintain optimal humidity levels and reduce the concentration of indoor pollutants.
Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) represent the cutting edge of this technology, providing efficient air exchange while conserving energy by transferring heat between incoming and outgoing air streams. These systems are particularly valuable in tightly sealed modern buildings where natural air exchange is limited.
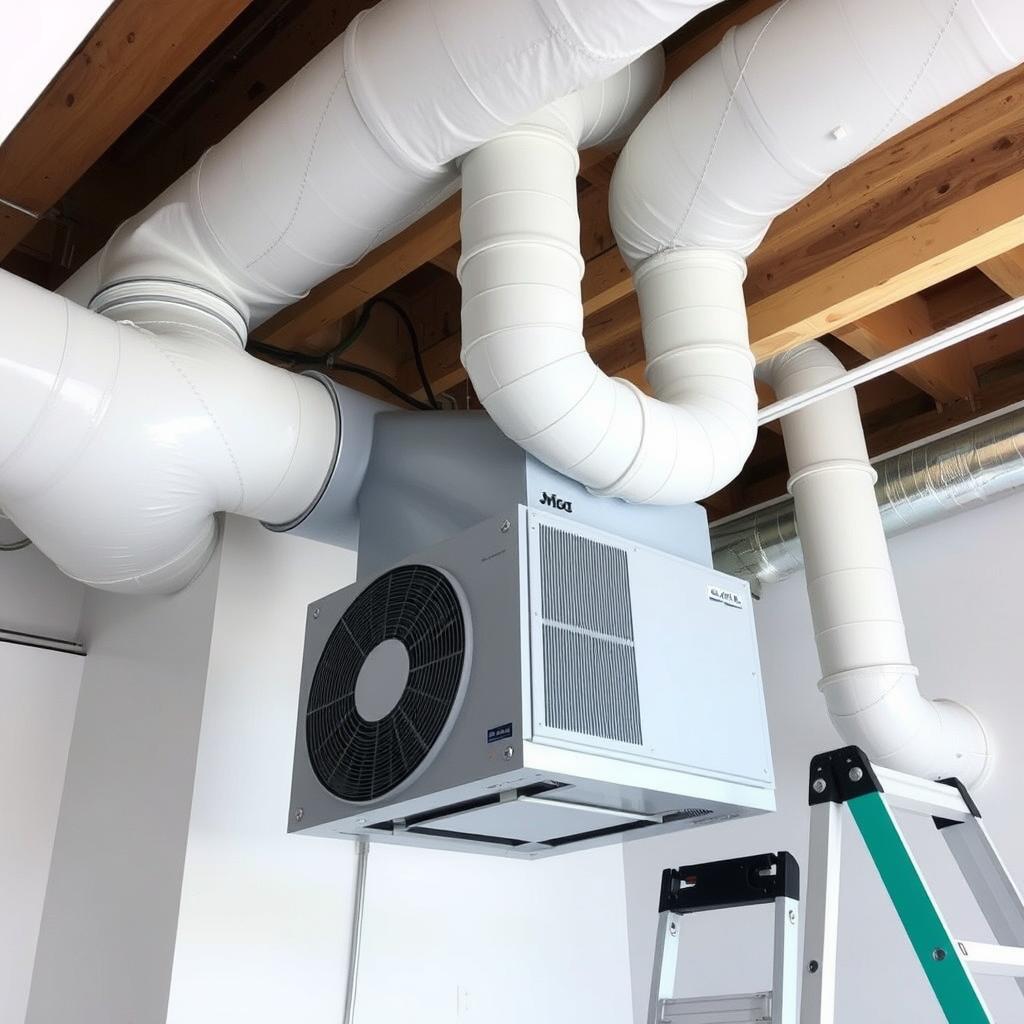

Smart Humidity Control Technology
Since moisture control is essential for preventing future mold growth, advanced remediation often incorporates smart humidity management systems. These systems use networks of sensors to monitor humidity levels throughout the building and automatically activate dehumidification or ventilation equipment when moisture levels approach the range that supports mold growth.
The most sophisticated systems integrate with home automation platforms, allowing property owners to monitor humidity levels remotely and receive alerts about conditions that might lead to mold growth. This proactive approach helps maintain healthy indoor air quality by addressing moisture issues before they can support mold development.
Case Studies: Successful Integration of Technology and IAQ Priorities
Examining real-world applications of advanced technologies in mold remediation provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of modern approaches. The following case studies demonstrate how integrating cutting-edge technology with indoor air quality priorities delivers superior outcomes.
Case Study 1: Historic Building Preservation
A 120-year-old library building suffered from recurring mold issues despite multiple traditional remediation attempts. By implementing thermal imaging, moisture mapping, and AI-driven analysis, remediation specialists identified previously undetected water intrusion pathways within the building’s complex structure.
The remediation plan incorporated dry ice blasting to preserve delicate architectural elements while eliminating mold, combined with a custom-designed ventilation system that maintained appropriate humidity levels without compromising the building’s historical integrity. Real-time air quality monitoring throughout the process ensured that valuable collections remained protected.
Results: Mold spore counts reduced by 99.7%, humidity stabilized between 40-50%, and no recurrence of mold issues after 24 months. The building’s indoor air quality now consistently exceeds library preservation standards.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Facility Remediation
A medical clinic discovered extensive mold growth following a plumbing failure. Given the sensitive nature of the environment and vulnerable patient population, maintaining exceptional indoor air quality during remediation was paramount.
The remediation team deployed advanced containment systems with continuous pressure monitoring, HEPA filtration with activated carbon, and botanical antimicrobial treatments. Portable air quality monitoring stations throughout the facility provided real-time data on particulate levels, VOCs, and microbial counts, with automated alerts if parameters exceeded medical-grade air quality standards.
Results: The facility maintained operations in unaffected areas throughout remediation with no reported air quality-related complaints. Post-remediation testing showed air quality exceeding healthcare standards, with particulate counts 65% below pre-incident levels.

Future Trends: The Next Generation of Remediation Technology
The field of mold remediation continues to evolve rapidly, with emerging technologies promising even greater effectiveness in addressing mold while prioritizing indoor air quality. Understanding these trends provides insight into how remediation practices will continue to advance.
IoT-Connected Monitoring and Prevention
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming mold prevention through networks of connected sensors that continuously monitor environmental conditions. These systems can detect subtle changes in humidity, temperature, and air quality that might indicate developing moisture problems or early-stage mold growth.
When integrated with building management systems, these networks can automatically adjust ventilation, dehumidification, and air filtration to maintain optimal conditions. Some advanced systems even incorporate predictive analytics that forecast potential moisture issues based on weather patterns, building usage, and historical data.

Nanotechnology in Mold Prevention and Remediation
Nanotechnology applications are emerging as powerful tools in both remediation and prevention. Nanostructured antimicrobial coatings can be applied to surfaces following remediation, creating microscopic barriers that prevent mold adhesion and growth. Unlike traditional antimicrobial treatments, these coatings can remain effective for years rather than months.
Research is also advancing on nanofiltration systems that can capture particles far smaller than those addressed by HEPA filters, potentially removing not just mold spores but also the microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) they produce. These technologies promise to further enhance indoor air quality during and after remediation.

Conclusion: The Synergy of Technology and Air Quality in Modern Remediation
The integration of advanced technologies with indoor air quality priorities represents a fundamental shift in how we approach mold remediation. This synergistic approach delivers outcomes that go beyond simply removing visible mold to create truly healthy indoor environments. By leveraging thermal imaging, AI-driven assessment, sophisticated air filtration, and real-time monitoring, modern remediation addresses both the immediate mold problem and its underlying causes.
The emphasis on indoor air quality throughout the remediation process ensures that occupants are protected during remediation and benefit from significantly improved air quality afterward. As technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more effective, efficient, and environmentally responsible approaches to mold remediation that prioritize the air we breathe.
For property owners facing mold issues, understanding these advanced approaches is essential for making informed decisions about remediation services. By choosing providers who integrate cutting-edge technology with a strong focus on indoor air quality, you can ensure comprehensive resolution of mold problems while creating a healthier living or working environment.
Contact Our Mold Remediation Experts
Concerned About Mold in Your Home?
Our experts use advanced technology to detect hidden mold and protect your indoor air quality. Don’t let mold affect your health and property.
Expert Mold Remediation Using Advanced Technology
Our certified technicians use the latest equipment and techniques to ensure complete mold removal while protecting your indoor air quality.
Learn More About Modern Mold Remediation
Download our comprehensive guide to understand how advanced technologies protect your indoor air quality during mold remediation.
Ready to Address Your Mold Concerns?
Our technicians use advanced technology to ensure complete mold removal while protecting your indoor air quality. Contact us today for a comprehensive assessment.
